Product Information
- Product Type
- Recombinant Protein
- Expression System
- E.coli
- Domain
- 77-233aa
- UniProt No.
- P01375
- NCBI Accession No.
- NP_000585.2
- Alternative names
- Tumor necrosis factor, Cachectin, TNF-alpha, Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 2, TNFSF2, TNF-a, TNFA, TNF
Product Specification
- Molecular Weight
- 17.5 kDa (158aa) confirmed by MALDI-TOF
- Concentration
- 1mg/ml (determined by Bradford assay)
- Formulation
- Liquid in. Phosphate-Buffered Saline (pH 7.4)
- Purity
- > 95% by SDS-PAGE
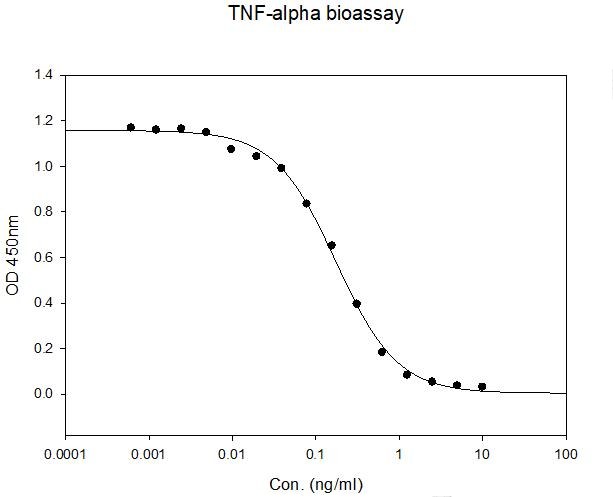
- Bioactivity
- Measured in a cytotoxicity assay using L-929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D. The ED50 range ≤ 0.2ng/ml.
- Endotoxin
- < 1 EU per 1ug of protein (determined by LAL method)
- Tag
- Non-Tagged
- Applications
- SDS-PAGE, Bioactivity
- Storage
- Can be stored at +2C to +8C for 1 week. For long term storage, aliquot and store at -20C to -80C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles.
Data
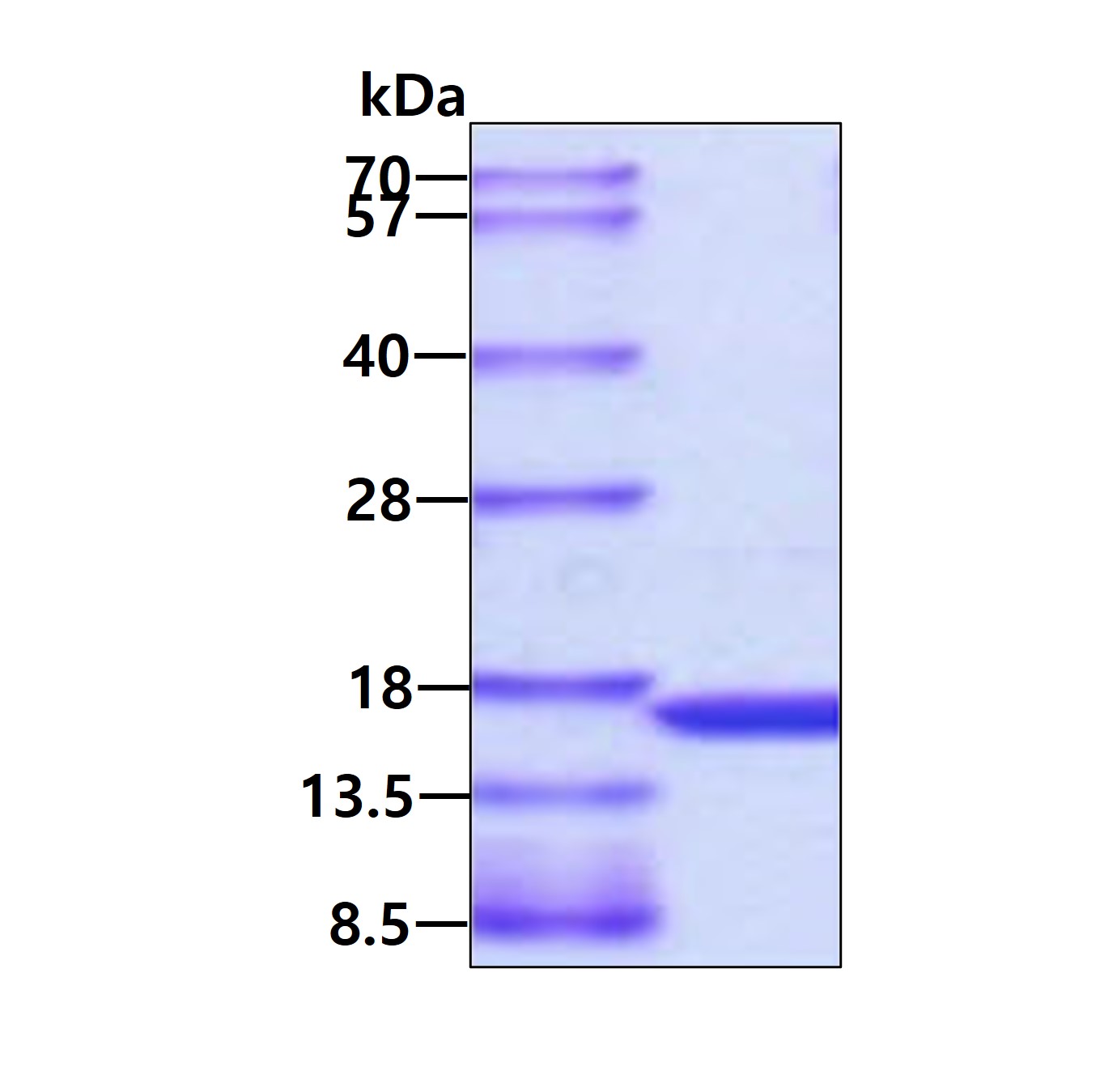
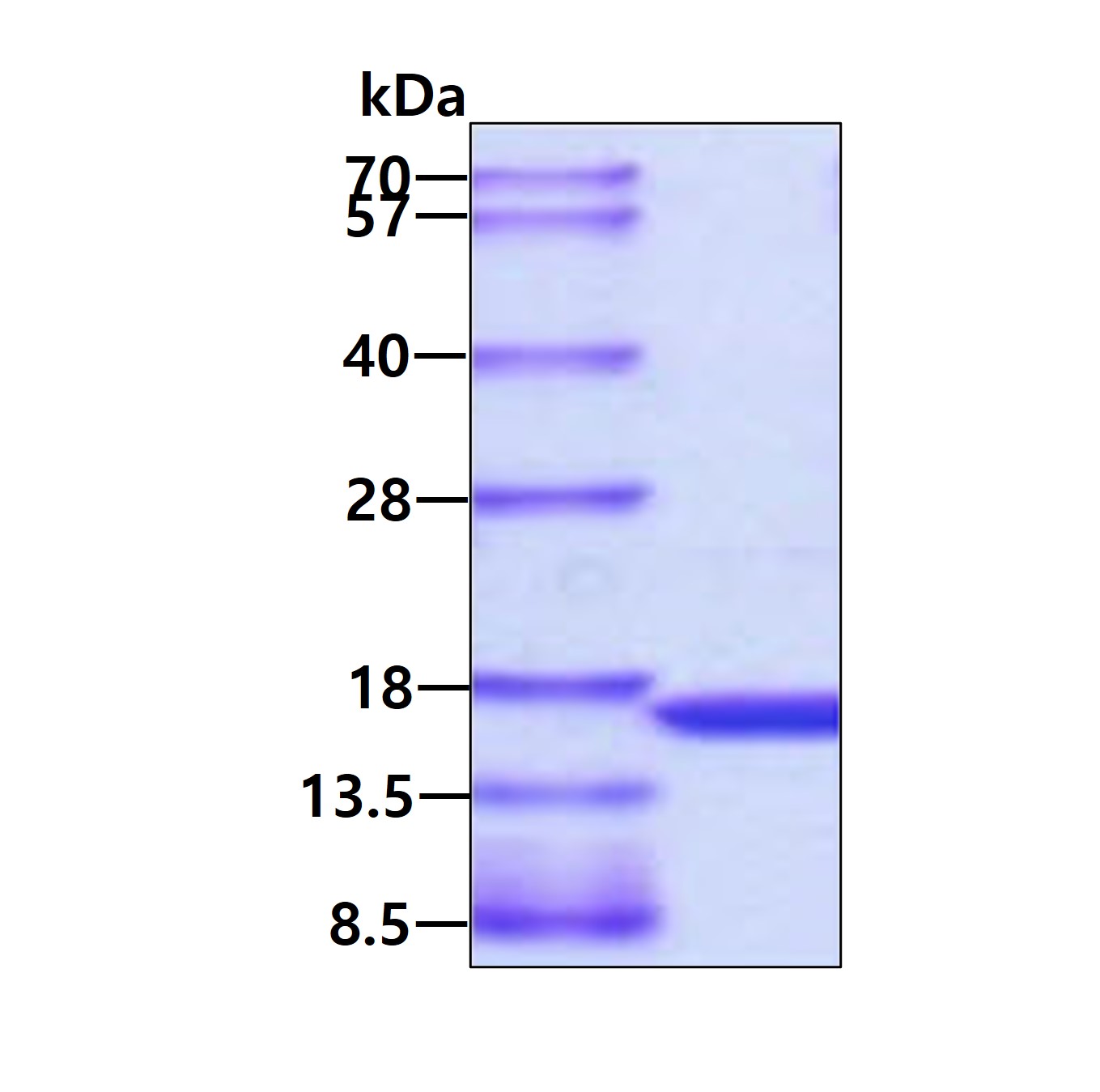
SDS-PAGE
3ug by SDS-PAGE under reducing condition and visualized by coomassie blue stain.
Biological Activity
Human TNF-alpha induces cell cytotoxicity in the L-929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D.
Related Publications
-
Kim JA, et al. A new lupane-type triterpene from the seeds of Panax ginseng with its inhibition of NF-κB. (Arch Pharm Res. 2012)
Nhiem NX, et al. Inhibition of nuclear transcription factor-κB and activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in HepG2 cells by cucurbitane-type triterpene glycosides from Momordica charantia. (J Med Food. 2012)
Song SB, et al. Inhibition of TNF-α-mediated NF-κB Transcriptional Activity in HepG2 Cells by Dammarane-type Saponins from Panax ginseng Leaves. (J Ginseng Res. 2012)
Liang C, et al. Oleanane-triterpenoids from Panax stipuleanatus inhibit NF-κB. (J Ginseng Res. 2013)
Cho K, et al. Inhibition of TNF-α-Mediated NF-κB Transcriptional Activity by Dammarane-Type Ginsenosides from Steamed Flower Buds of Panax ginseng in HepG2 and SK-Hep1 Cells. (Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014)
Thao NP, et al. Inhibition of NF-κB transcriptional activation in HepG2 cells by diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia maxima. (Arch Pharm Res. 2014)
Thao NP, et al. NF-κB inhibitory activity of polyoxygenated steroids from the Vietnamese soft coral Sarcophyton pauciplicatum. (Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014)
Li W, et al. Anti-Inflammatory and PPAR Transactivational Effects of Oleanane-Type Triterpenoid Saponins from the Roots of Pulsatilla koreana. (Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014)
He F, et al. Antitumor effects of dammarane-type saponins from steamed Notoginseng. (Pharmacogn Mag. 2014)
Yang SY, et al. NF-κB Activation and PPAR Transactivational Effects of a New Aliphatic Acid Amide from Pericarps of Zanthoxylum piperitum. (Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2014)
Sun YN, et al. NF-κB Inhibitory Activities of Phenolic and Lignan Components from the Stems of Acanthopanax divaricatus var. albeofructus. (Natural Product Sciences. 2014)
Sun YN, et al. Nuclear Factor Kappa B Activation and Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Transactivational Effects of Chemical Components of the Roots of Polygonum multiflorum. (Pharmacogn Mag. 2016)
Sun YN, et al. Isolation and identification of chromone and pyrone constituents from Aloe and their anti-inflammatory activities. (J Funct Foods. 2016)
Sun YN, et al. A new phenolic derivative with soluble epoxide hydrolase and nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitory activity from the aqueous extract of Acacia catechu. (Nat Prod Res. 2016)
Kwak MS, et al. Peroxiredoxin-mediated disulfide bond formation is required for nucleocytoplasmic translocation and secretion of HMGB1 in response to inflammatory stimuli. (Redox Biol. 2019)
Jang SH, et al. Sinapic acid alleviates inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) through localization of tight junction proteins by direct binding to TAK1 and improves intestinal microbiota. (Front Pharmacol. 2023)
Kim S, et al. Hybrid nutraceutical of 2-ketoglutaric acid in improving inflammatory bowel disease: Role of prebiotics and TAK1 inhibitor. (Biomed Pharmacother. 2024)
Note: For research use only. This product is not intended or approved for human, diagnostics or veterinary use.